Vision-Informed Multi-Modal Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning for Active Distribution Network Scheduling
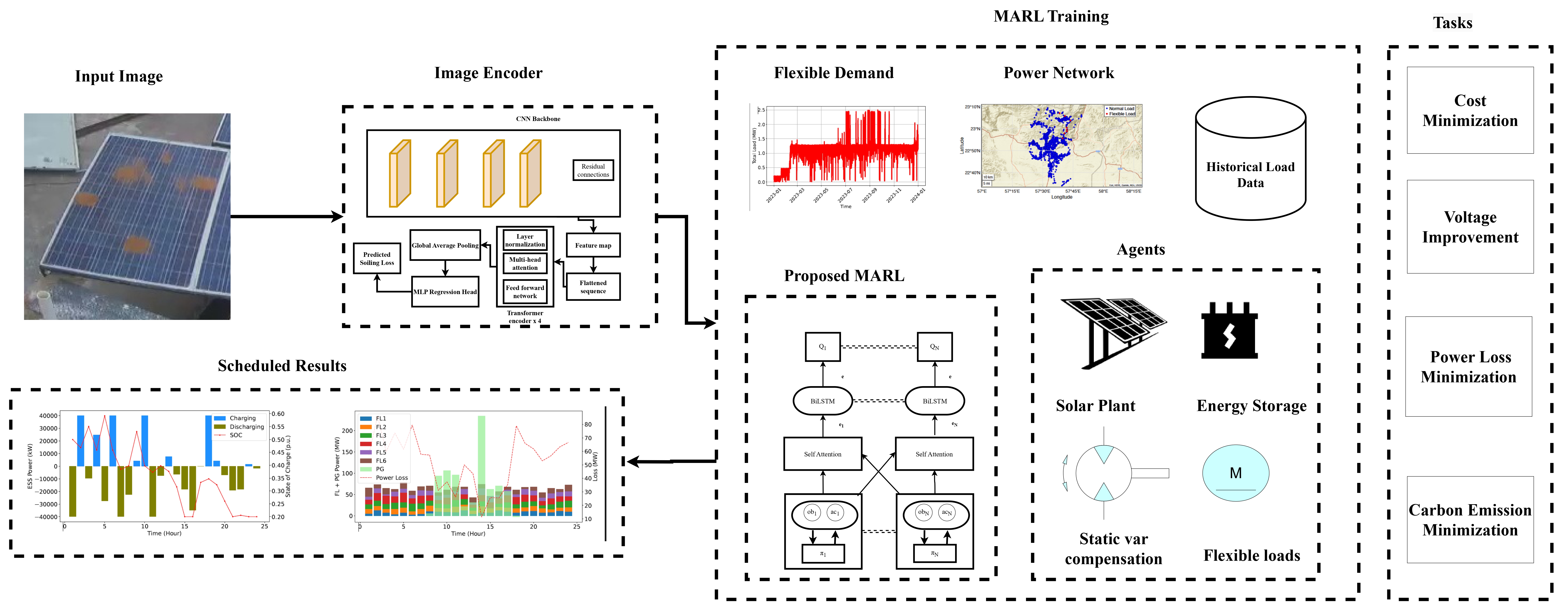
- Introduced the first vision-aware framework for distribution-network scheduling by integrating image-derived soiling features into the cooperative control of solar plants, energy-storage systems, static-var compensators, and flexible water-pumping loads.
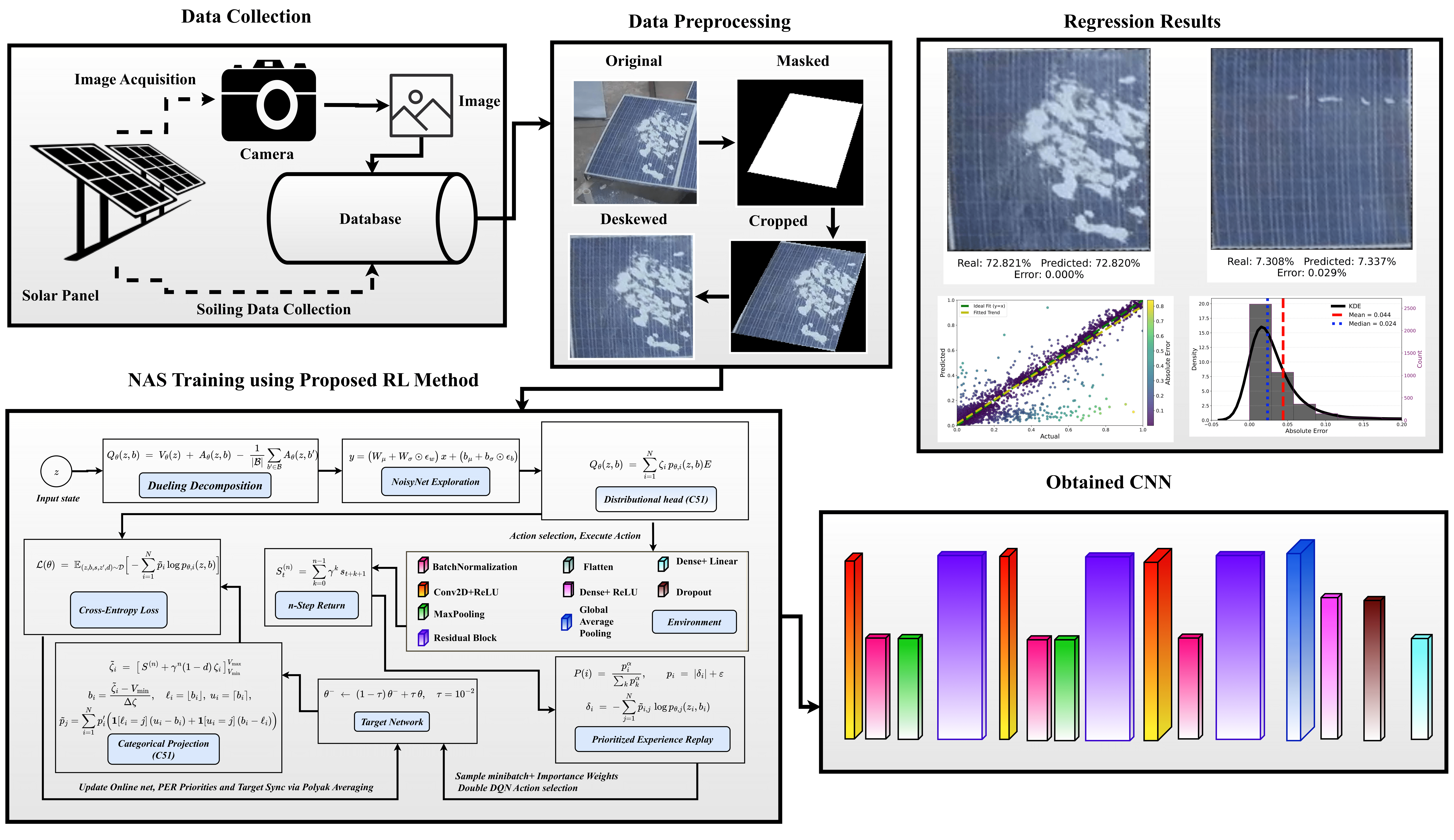
- Built a CNN–ViT encoder for real-time generation loss estimation and fused it with grid measurements to enable a perception–control scheduling loop.
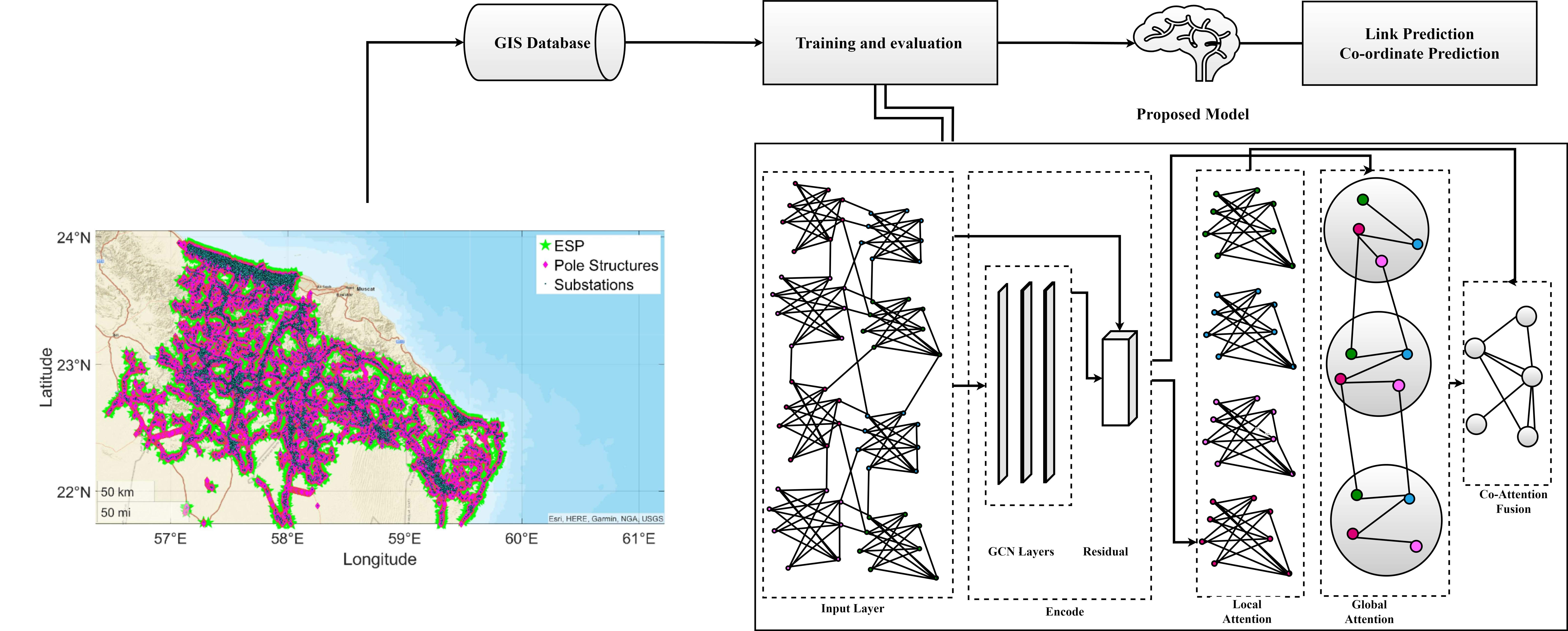
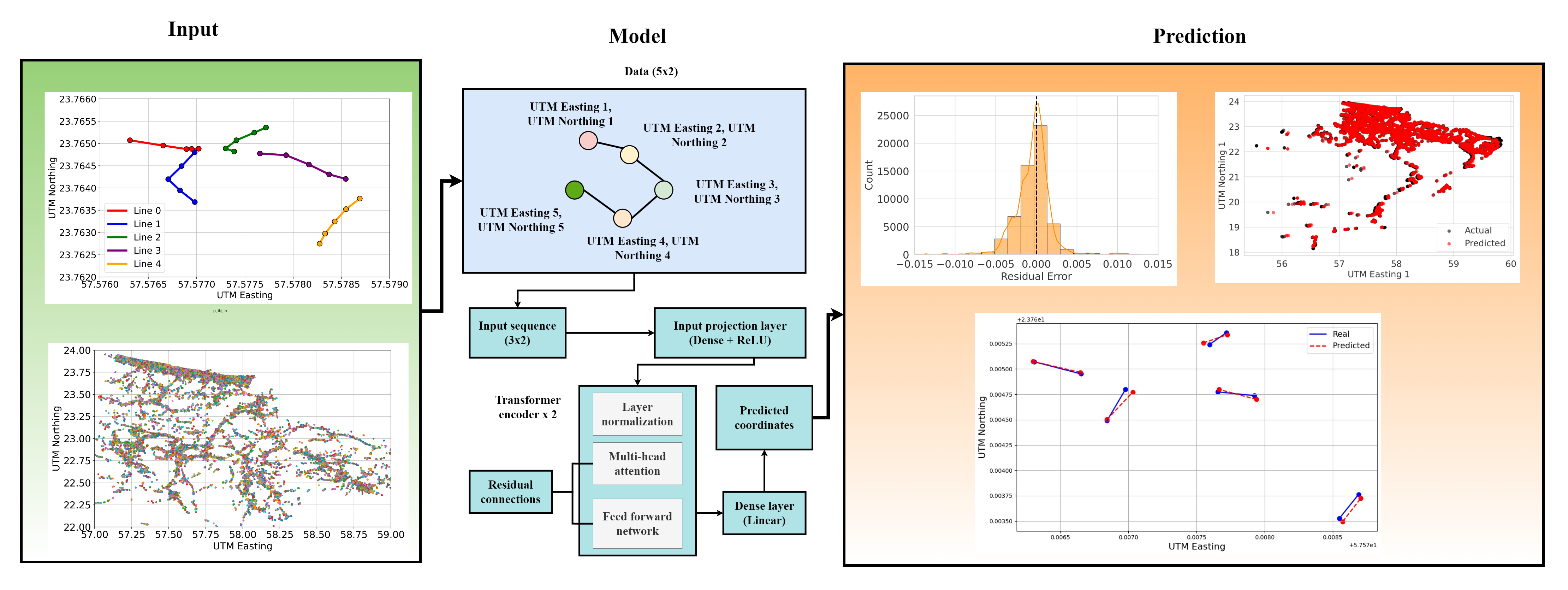
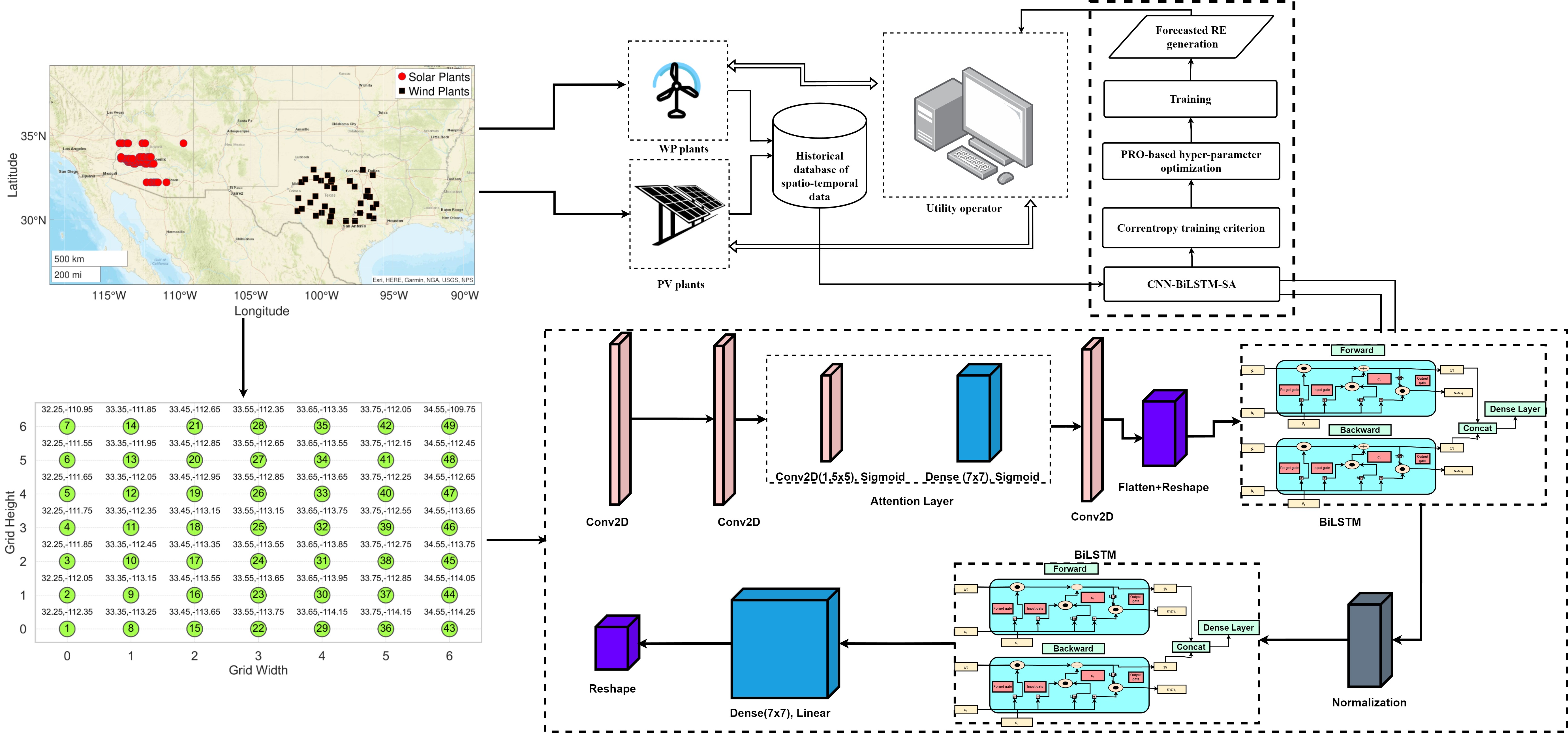
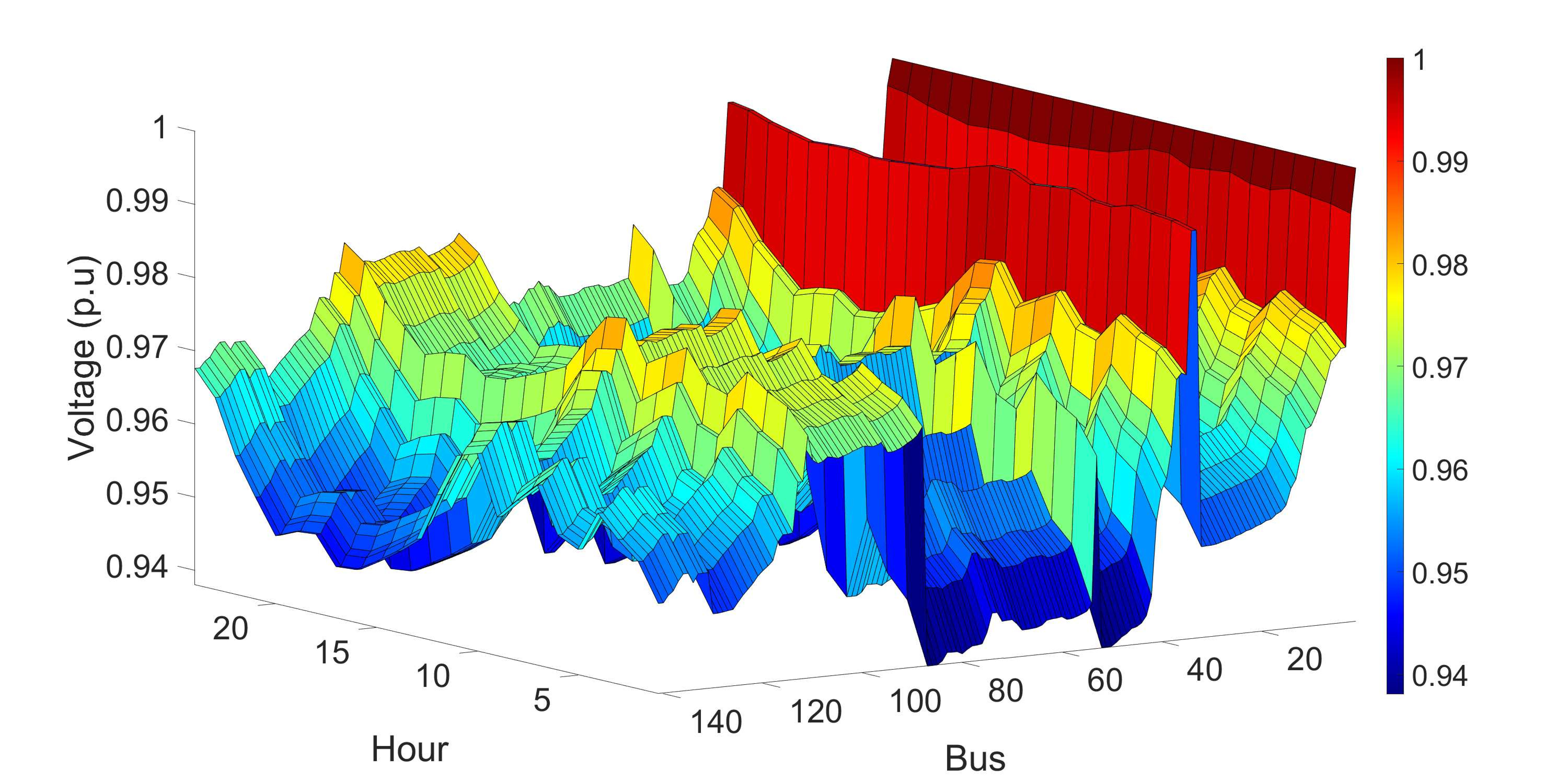
- Implemented the architecture in PyTorch 2.6. The framework was validated using the DeepSolarEye dataset (44K annotated solar images) for soiling regression and applied to the realistic 2289-bus Nizwa grid in Oman, collected from Mazoon Electricity Company (MZEC).
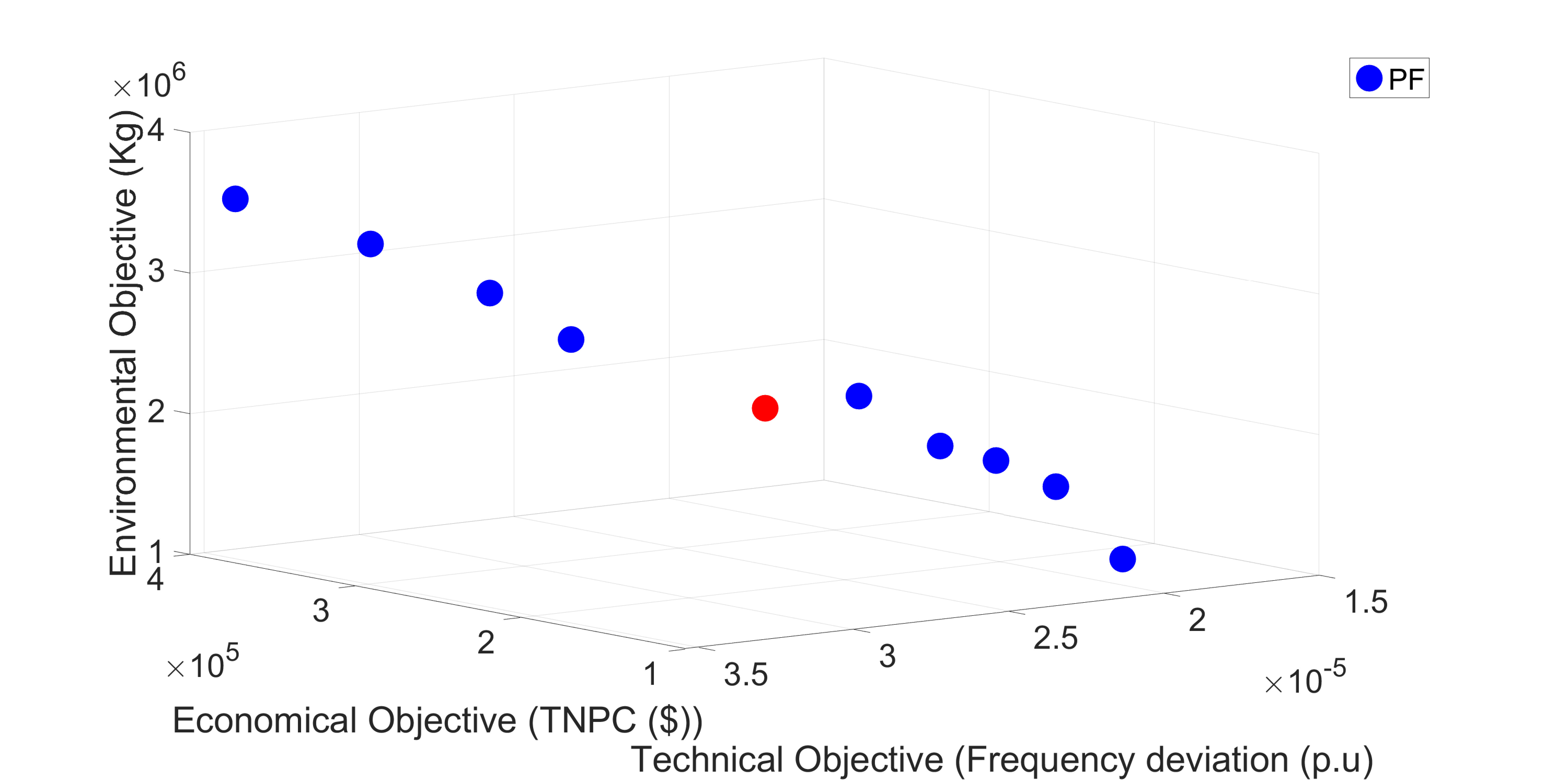
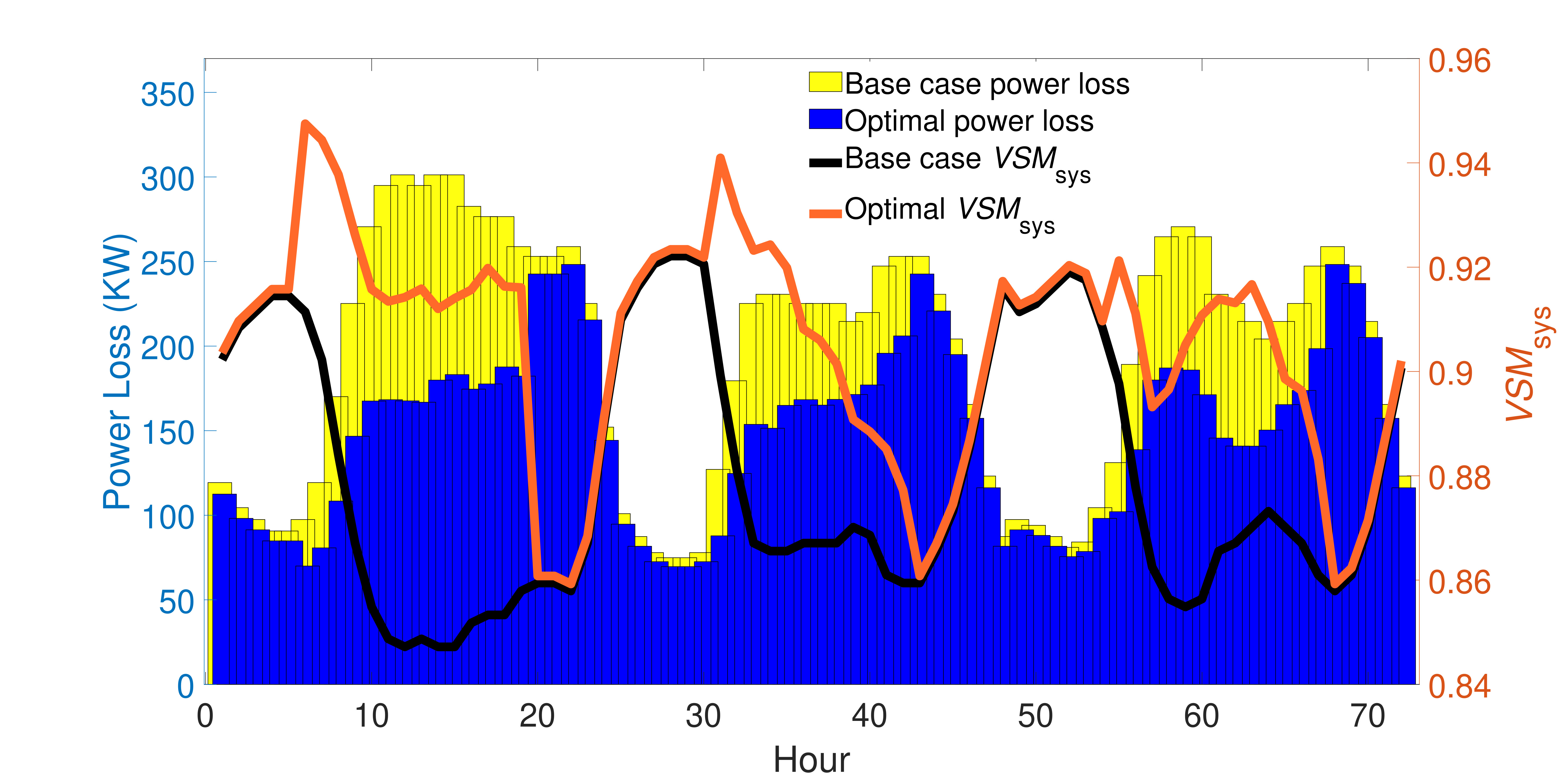
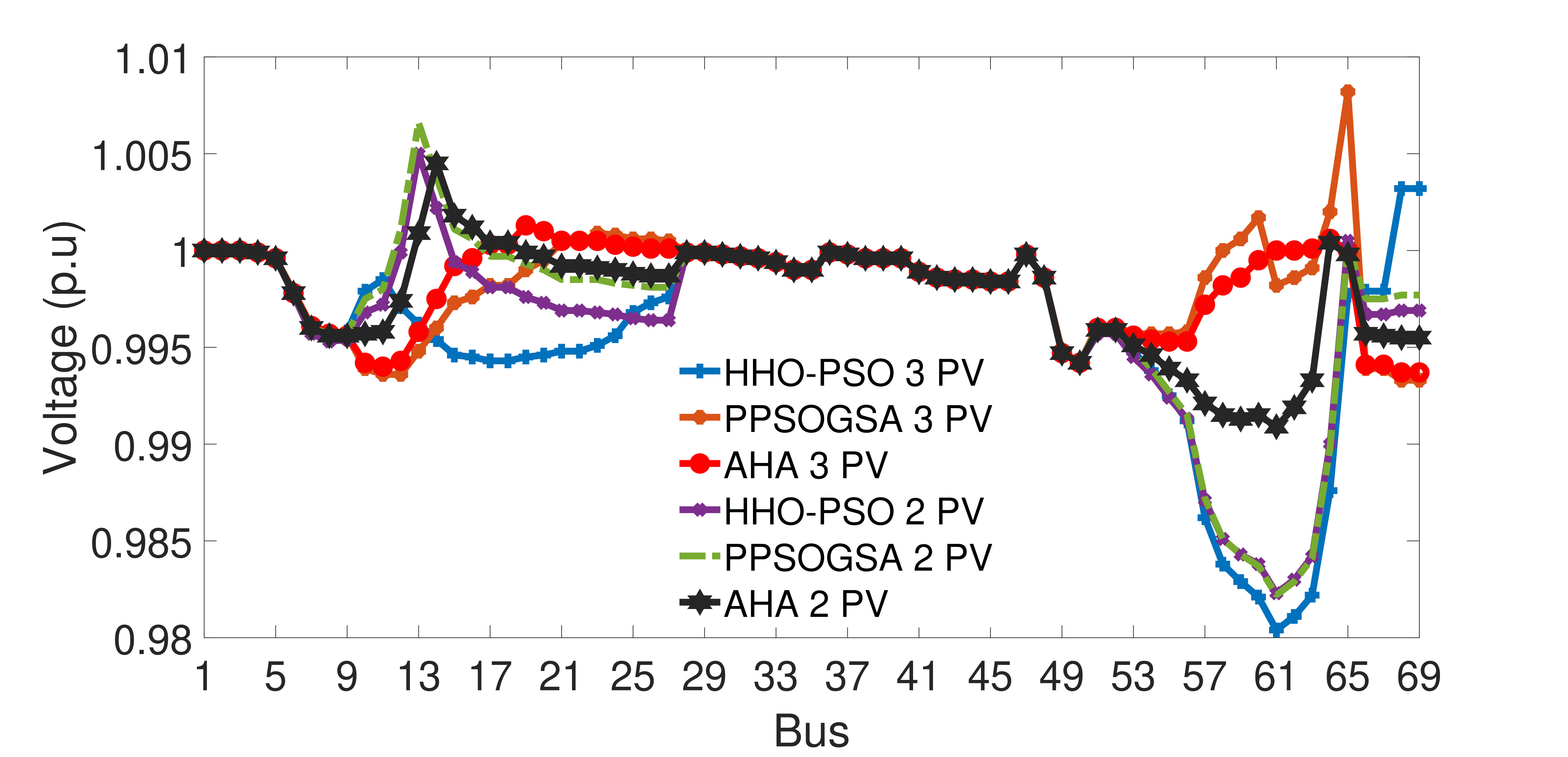
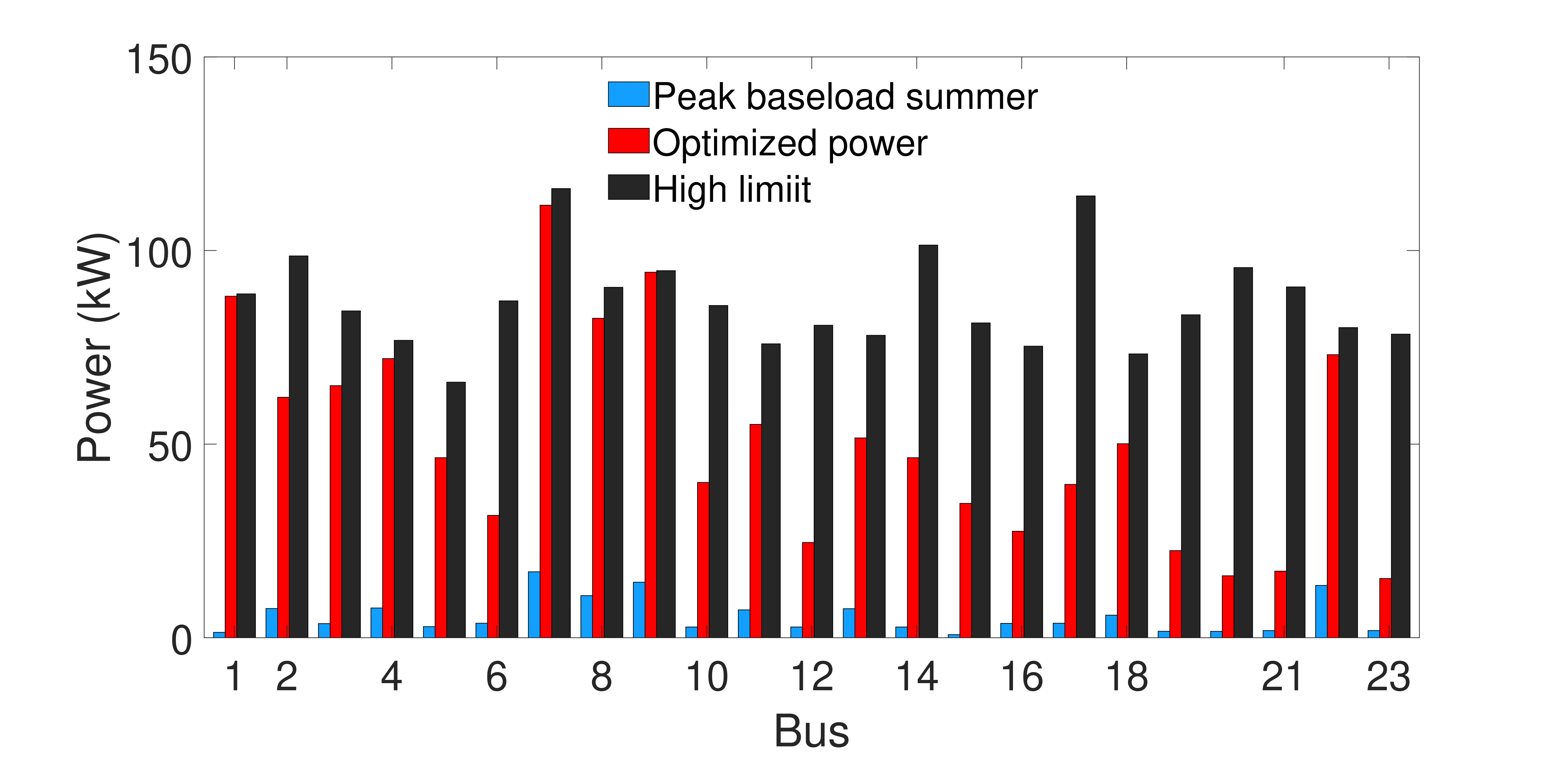
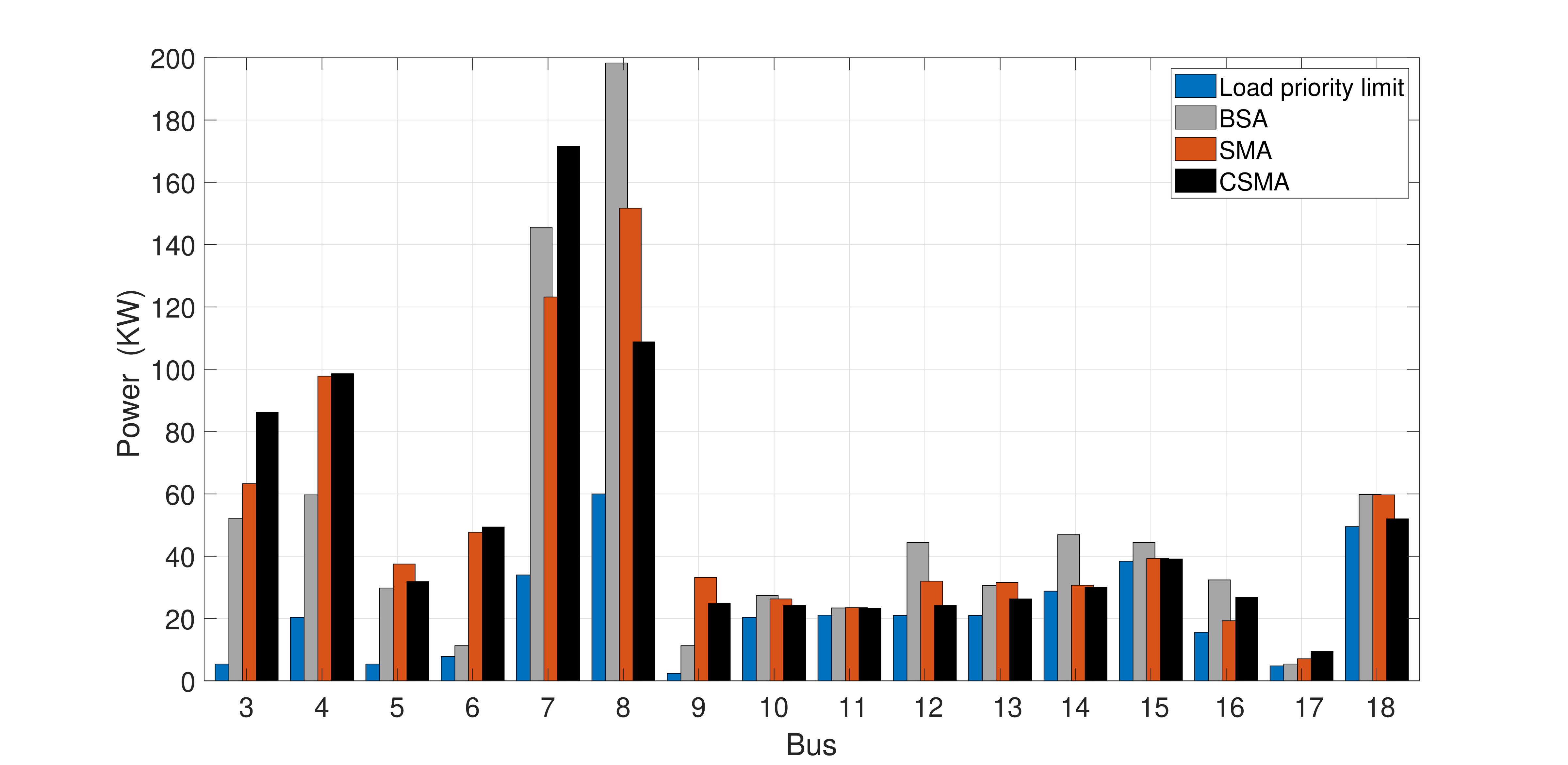
- Achieved R² = 0.91; reduced operational costs by 7.1%; lowered losses by 19.2%; decreased carbon emissions; and improved renewable-to-load alignment by 15%.